Working with chemicals and liquid photopolymer resins involves safety hazards that can be effectively minimized by following the guidelines in the Safety Data Sheets (SDS) and using appropriate Personal Protective Equipment (PPE).
Understanding Risks and Sensitivities of Liquid Photopolymer
Despite precautions, eye and skin irritation or allergic skin sensitization can occur when handling liquid photopolymers, detergents, and processing solutions. It’s crucial for employers to recognize that some workers may be more sensitive and require individualized precautions to avoid allergic reactions.
Safe Work Practices
Implementing general guidelines for good industrial hygiene and safe work practices is essential when using chemicals and liquid photopolymer resins.
Skin Protection
Avoid skin contact by wearing protective gloves. Disposable gloves are effective, and seamless or vinyl gloves offer good protection for short durations if cleaned between uses. Remember, gloves do not last indefinitely and should be replaced when necessary. Washing hands after removing gloves and before leaving the work area is crucial to prevent chemical spread to other body parts.
Clothing
Contaminated clothing should be removed and laundered before reuse. If washed at home, these clothes should be cleaned separately to avoid cross-contamination. Any irritation, despite these precautions, should be promptly reported to medical or first aid personnel.
Eye Protection
To prevent chemical splashes, always wear safety glasses when using chemicals or liquid photopolymer resins. The AVantage® photopolymer resins are processed using UV light exposure units, and exposure to UV light can cause photokeratitis, leading to increased tears and a painful sensation similar to having sand in the eyes. UV protective glasses should be worn during testing and maintenance of UV light sources.
Inhalation
Ensure adequate ventilation in areas where AVantage® photopolymers and chemicals are used. Inhalation of dust, mist, fumes, or vapors should be kept below Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) prescribed levels. Refer to OSHA venting requirements for detailed standards.
Ingestion
Food and drink should never be stored, prepared, or consumed in areas where they may be exposed to industrial processing chemicals.
Good Housekeeping Practices
Maintain cleanliness throughout the plant to prevent handling problems, abuses, and carelessness. Clean spills immediately using appropriate PPE to prevent chemical exposures.
Reclaiming and Reusing Liquid Photopolymer Resin
The ability to reclaim and reuse liquid photopolymer resin sets this product apart from sheet plates, offering a significant financial benefit to customers.
Equipment and Procedures
Equipment and procedures for collecting and handling reclaimed liquid photopolymer resin can vary, but with careful handling, reclaimed resin can produce high-quality printing plates by following some basic guidelines.
Collection
Protect the photopolymer resin from UV light by using opaque collection containers and illuminating the room with yellow or UV-filtered lights.
Filtration
Reclaimed liquid resin needs to be filtered to remove gels, solid resin pieces, or foreign matter. Place the filter in an accessible position, either in line or at the mouth of the collection container. Filtering with cheesecloth, aluminum, or stainless steel using 100-200 mesh is recommended, and the filter should be cleaned weekly. Overflow resin can be collected from the overflow tray, screened, and mixed with the reclaim resin.
Mixing
For direct use in a bucket system, aerate the resin before use and mix it with virgin resin. In a tank mixture, blend reclaimed resin at a ratio of 3:1 (3 parts virgin resin to 1 part reclaim). Add resin at the end of the day, pouring reclaim first, followed by equal amounts of virgin resin. Let the system’s mixer or blender run overnight to ensure thorough blending. Add reclaimed and virgin resin daily to avoid large volumes of reclaimed buildup.
Safety
Always use proper Personal Protective Equipment (PPE), including gloves and safety glasses, when handling liquid resin from the reclaimer to the storage tank.
By following these guidelines, you can effectively reclaim and reuse liquid photopolymer resin, ensuring high-quality printing plates and enjoying the financial benefits of reduced waste.
AVantage® Resins and Film Negative Materials
Specifications and recommendations for using negative film are detailed here to obtain optimum quality reproduction when using AVantage® photopolymer resins.
Base film for plates should be clear or a light matte surface. It should be smooth and free of handling defects such as nicks and dings. A heavy matte material may diffuse the UV light too much and fill reverses.
Using a transmission densitometer to determine the measurement, the optical density in the clear area of the negative should be 0.05 or less. The black area of the negative should be 4.0+ to avoid reduction in etch deep of the character or midtone screens and shadows. The image should be right reading, requiring the emulsion side up on the negative (bronze plate production requires wrong reading negative so the final product will be right reading).
Negative thicknesses are 4.0 mil and 7.0 mil. The film can be clear or matte format. Clear film is recommended to ensure the reproduction of the negative in a high quality. Do not mix negative thicknesses on a liquid exposure unit because the resulting plate will note the 3.0 mil difference in the film.
A one-piece negative is recommended for plate making. Overlapping, stripping, or taping negatives together may cause a plate tolerance problem.
A high-contrast negative is needed in order to properly expose the photopolymer resin, reproducing the desired dot or screen without halos or fringes. The UV light will transmit through the character area for quality reproduction with quality structure support. Using an exposure control guide will help monitor the plate quality on a daily basis.
Feed and Bleed Setup:
The starting bath should be charged into the bath. If not sure please reference Tech Tip on washout bath formulation for your sized washout unit.
The Feed and Bleed requires four or five additions to the bath on each wash cycle. There is water, detergent, defoamer, and developer. If AVenhance is being used it is pumped in along with the other chemicals.
Feed and Bleed amounts to washout bath size:
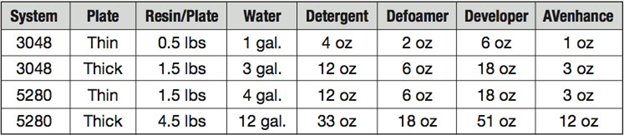
Note: AVenhance also acts as a defoamer, so be aware that the suggested amount of defoamer can be reduced, possibly by as much as 50%.
Plate Set-up Formula
All photopolymer resins shrink slightly when exposed and cured during the plate making process. The AVantage® line of liquid polymers is no different.
The resin shrinkage rate must be accounted for in the setup to set the proper shim pack. First and foremost is the desired target plate thickness. Next is the film thickness being used to make the printing plate. There are many different types of film being used these days to produce printing plates. There is the old standard silver film at 4 mil and 7 mil thickness. The new AVSTAR printed film sold by Anderson & Vreeland, Inc. is available in 5.5 mil and 8 mil film bases. The system uses a piece of cover film to protect the negative and seal it to the lower glass. The cover film is generally 0.7 mil thick.
The following equation will set the shim pack to make the desired plate requirements using AVantage® resins:
Examples:
- 67 mil + 1 + 1.5 + 4 mil silver = 73 mil
- 67 mil + 1 + 1.5 + 5.5 printed film = 75 mil
- 250 mil + 1 + 5 + 7 mil silver = 263 mil
- 250 mil + 1 + 5 + 8 mil printed film = 264 mil
Note: Plate exposure times will be different for silver film and printed film because printed film has a UV coated layer to generate the density needed with the ink coating to prevent the UV from coming through the dark black areas of the negative.
Closing Thoughts
AVantage® chemicals and liquid photopolymer resins should be treated with the same care as other industrial chemicals. Always review and follow the SDS literature before using any chemicals. Adopting safe work practices and proper disposal of waste chemicals according to local, state, and federal regulations is essential. For specific handling and disposal information, refer to the product’s SDS sheets.
By adhering to these guidelines, you can ensure a safer working environment and minimize the risks associated with handling resins and chemicals.
Ensure the highest safety and quality standards in your printing processes. Contact Anderson & Vreeland today for expert guidance.
Call us at (866) 282-7697


